Common Troubleshooting Questions
Wireless signal degrades with distance and obstructions.
Common signal impairments include walls, ceilings, metal, concrete, cinder blocks, fluorescent lights, microwaves, furniture, etc. While the GigaCenter has been optimized to provide wireless coverage for most applications, there may be dependencies based on the location where the device is installed.
Please contact us for troubleshooting assistance.
If the RESET button is depressed for less than 5 seconds, it resets the unit using the current configuration settings.
Pressing the RESET button on the back of the unit for at least 5 seconds, or access the “Restore Defaults” reset radio button located in the “Utilities” section of the Embedded Web Interface.
Pressing the WPS button broadcasts the GigaCenters credentials (network password) to other WPS capable devices for a period of 2 minutes, allowing these devices to gain access to the wireless network.
Yes, the unit is set up with “WPA2 Key” Wi-Fi security. Login/password credentials are printed on the inventory label and the product label affixed to the device.
Try setting up the wired connection and configuring the wireless encryption again.
Press the reset button of the wireless router for at least five seconds. Device reverts to factory default settings custom configuration options (such as SSID names) are reset as well.
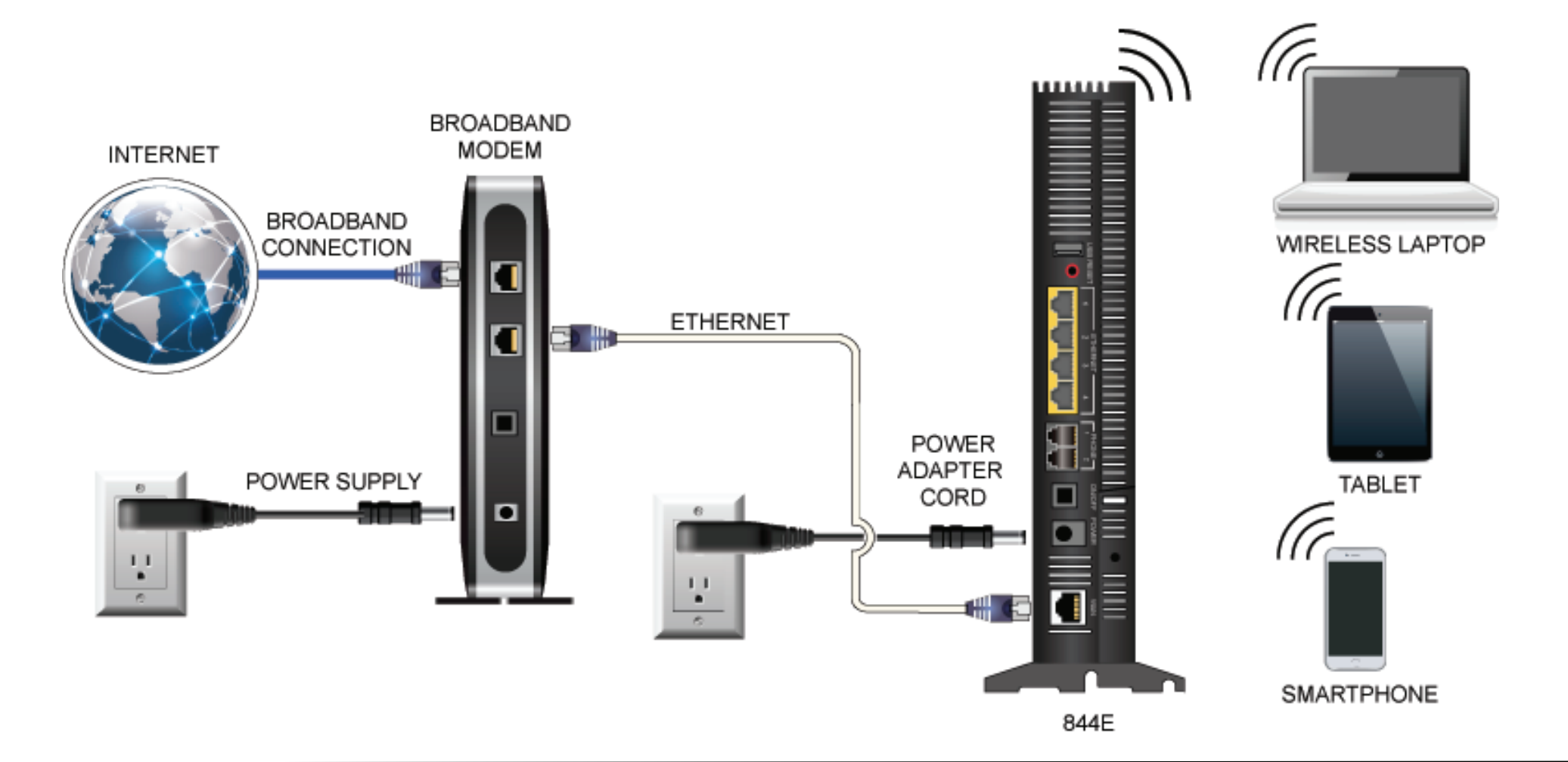
Modems vs. Routers
Most people use their home network to access the Internet, but many have no idea how these networks work. The modem connects your home to the Internet, while a router creates the network inside your house.
Modems bring the Internet to your home
A modem is a device that connects your home, usually through a coax cable connection, to your Internet service provider (ISP), like RTC. The modem takes signals from your ISP and translates them into signals your local devices can use, and vice versa. The connection between your house and the Internet is known as a wide area network (WAN). Each modem has an assigned public IP address that identifies it on the Internet.
Routers bring the Internet to your devices
A router connects your devices to each other and, in hard-wired setups, to the modem. The router connects to your modem and then to your devices (laptops, smart TVs, printers, etc.) via either an Ethernet cable or Wi-Fi signal. The router creates a local area network (LAN) within your house, allowing your devices to share files and peripherals like printers. The router manages all the information going to and from each device and the modem and makes sure it all ends up safely in the right spot. However, a router doesn’t need to connect to a modem to function. You can choose to create a LAN without Internet access.
Router Set-Up and Troubleshooting
Power Cycling or Restarting
Most common Wi-Fi issues can be solved by power cycling or restarting your modem. The process is quick and does not require you to lose your home network settings. During the restart process, you will simply power off the modem by unplugging it from the power supply, wait 30 seconds, power it back on, and restart your computer.
Reset
During a reset, your modem and router will be reset to the manufacturer’s original settings, including your Wi-Fi name and password. A reset requires using a small object, such as the tip of a pen or pin, to hold in the small reset button on the back of your modem until the lights power off and on. This also resets all of the configurations by your Internet Service Provider and requires provisioning of the device.
You rarely want to do this as it will cause all of the settings to be wiped from your device, meaning your internet will be down until your Internet Service Provider can reprogram the device. Resetting certain modems or routers will require a truck roll and may result in additional charges.
Router LED Status Indicators
Knowing how the blinking boxes plugged into your wall work can help you to get the Internet up and running again the next time there’s a power outage or connection disruption.

Power – If solid GREEN, unit is powered up and operational. If solid AMBER or RED, please contact us and we will connect you with a technician. If flashing AMBER, the device is undergoing a software update – do not power off if in this state.
Broadband – If solid GREEN, a broadband connection has been established.
Service – If solid GREEN, Internet service has been established. If solid AMBER, the device is in “Walled Garden” mode (your browser may be redirected to our website). If solid RED, the device has failed to receive an IP address or a PPPoE session has not been established.
Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz, Wi-Fi 5 GHz, Ethernet 1-4, Phone 1-2, USB – If solid GREEN or flashing GREEN, services are provisioned or devices are connected and active.




